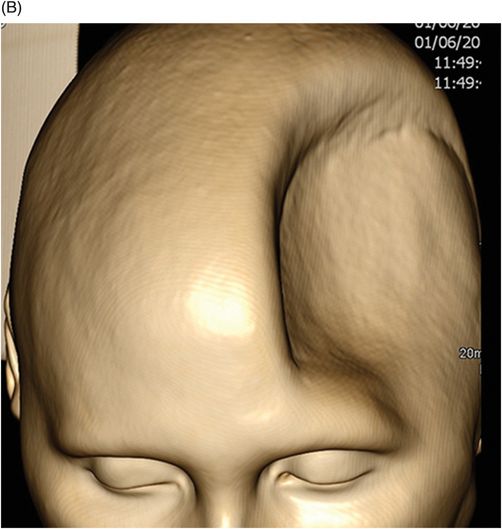
Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome
Sinking skin flap syndrome. He was diagnosed with sinking skin flap syndrome consistent with altered mental status and a sunken skin flap with increased midline shift. SUNKEN SKIN FLAP SYNDROME. A case presentation and review Dr Bipin Bhimani Well Care Hospital Rajkot 2.
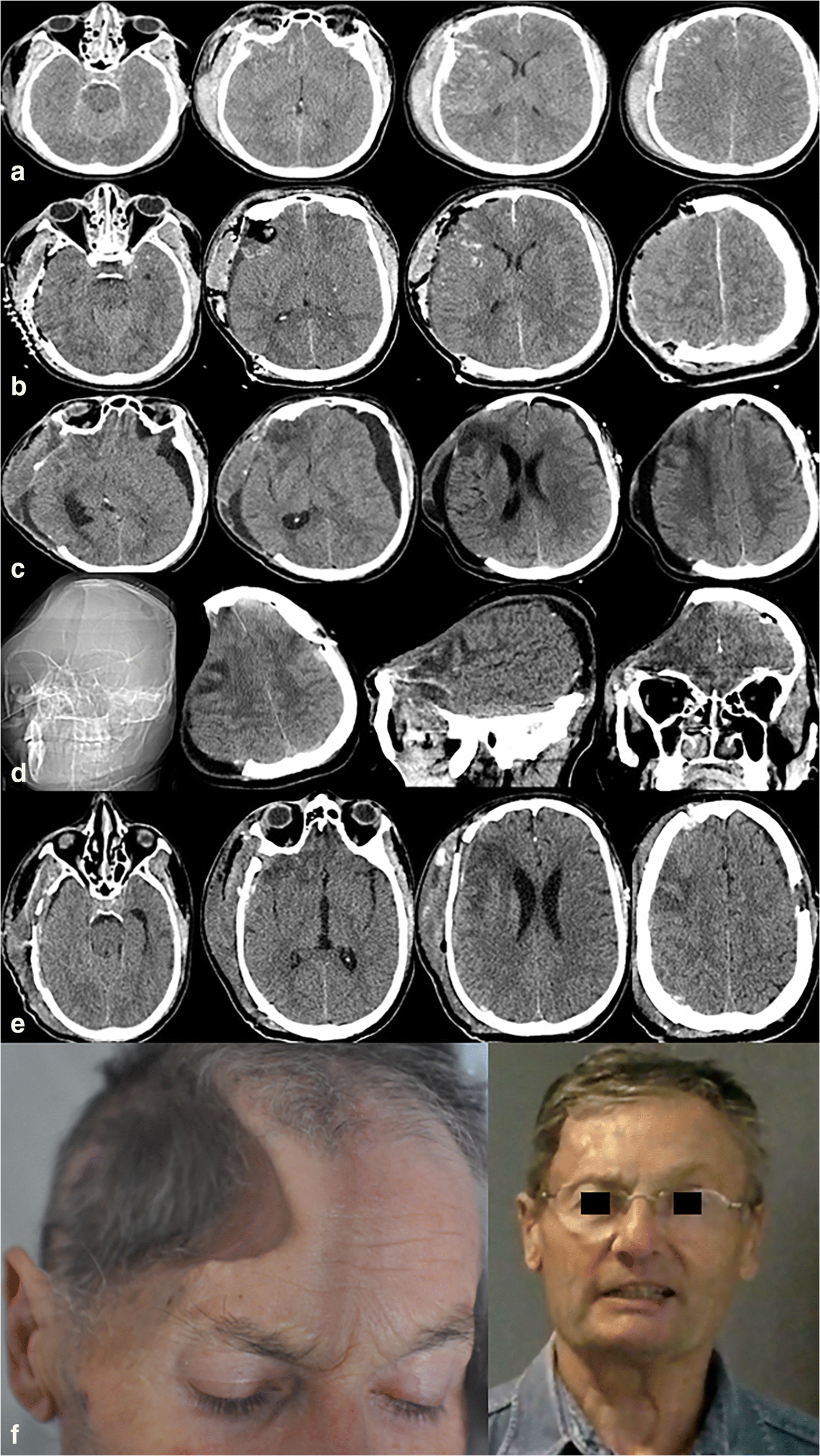
Cerebral hemodynamic is compromised in the presence of a cranial defect by the following mechanisms. 1 2 3 4 5 This phenomenon may result from atmospheric pressure gradient that may be aggravated by CSF diversion CSF hypovolemia. Case presentation Young male patient 32 years old He had Right MCA territory infract 3.
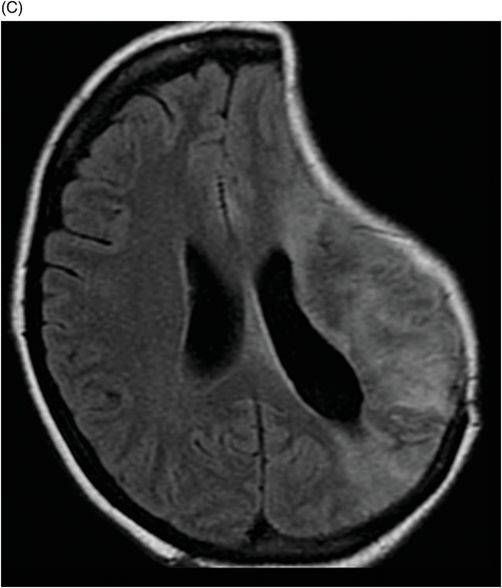
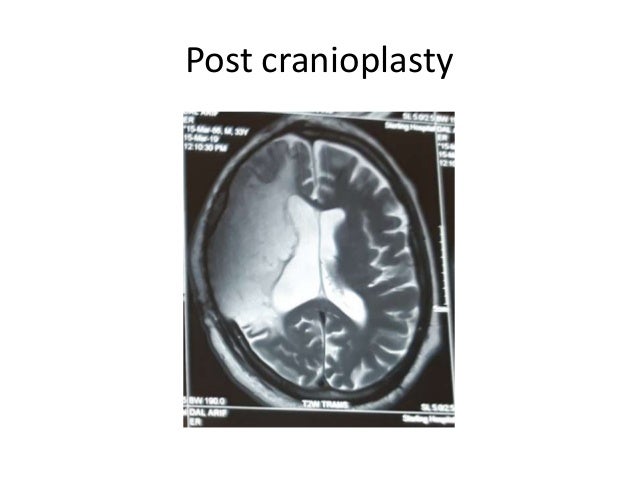
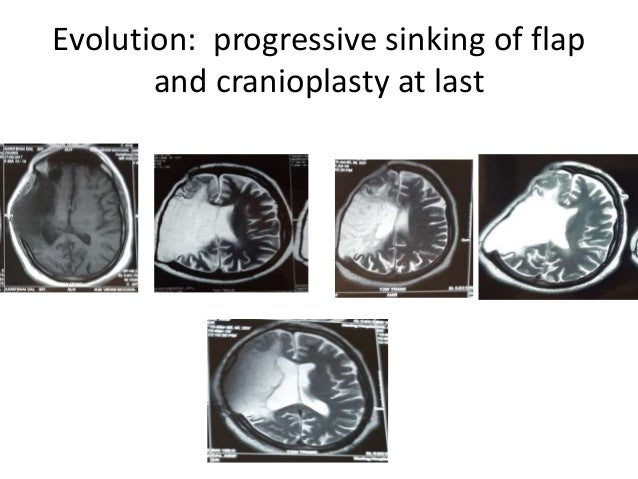
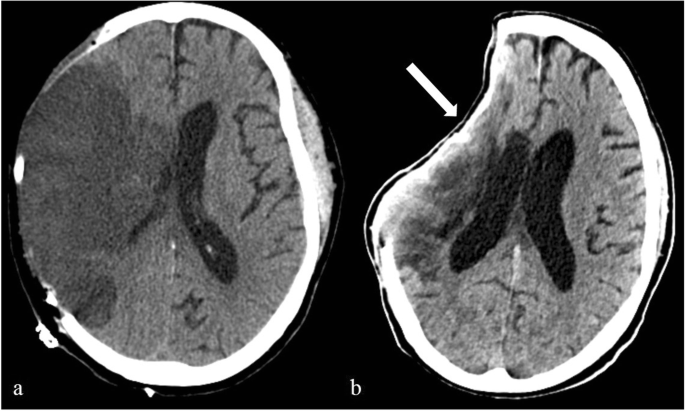
The sinking skin flap syndrome SSFS is characterized by neurological symptoms headache epileptic seizures vertigo dysesthesias or paresis following extensive decompressive craniectomy which improve after cranioplasty. This may result in subfalcine andor transtentorial herniation. The sinking skin flap syndrome SSFS is defined as a secondary neurological deterioration which cannot be attributed to the primary illness and which occurs in the presence of a sinking skin flap in patients with large craniectomies.
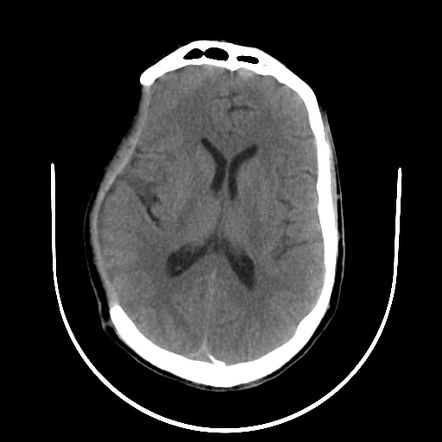
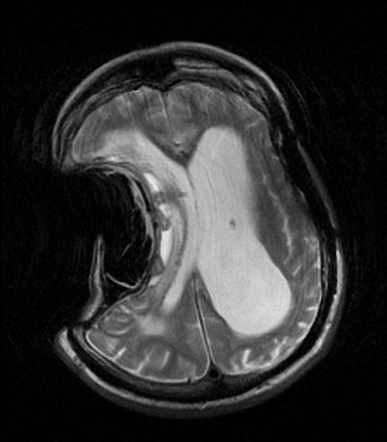
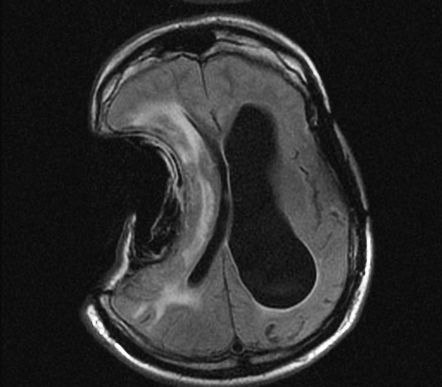
Sinking skin flap syndrome is defined as a series of neurologic symptoms with the skin depression at the site of cranial defect which develop several weeks to months after large external cerebral decompression. Sinking skin flap syndrome or syndrome of the trephined can occur in patients with prior hemicraniectomies in the setting of post-operative lumbar puncture or ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement. Right MCA Infarct 4.
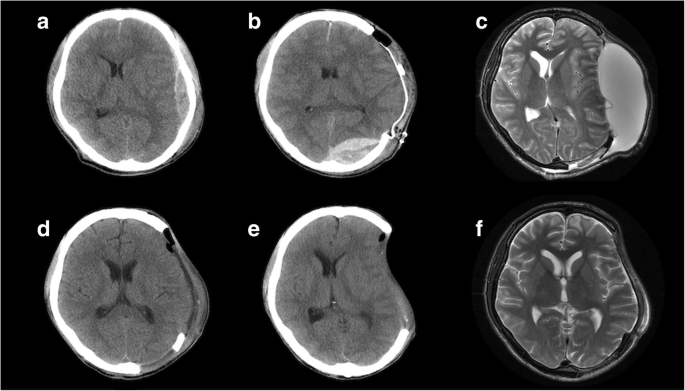
Hereby we report for the first time that DC patients with LD can progress to SSFS or PH. Independent of the consequences of the original aetiology that necessitated the craniectomy the bone defect alone may be the cause of the symptoms called trephined syndrome or. 22913 - moderate size infarct thrombolysed with IV tPA 5.
Despite treatment with Trendelenburg positioning and appropriate fluid management the patient continued to decline and an epidural blood patch was requested for treatment. Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome 1. This results in displacement of the brain across various intracranial boundaries.
Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome Published. He syndrome of the trephined or the sinking skin flap SSF syndrome is a rare complication after a large skull bone defect1 It consists of a sunken skin above the bone defect with neurological symptoms such as severe headaches mental changes focal deficits or seizures12 The SSF may.
The subarachanoid space is obliterated over the cortex in that area by scarring of.
Despite treatment with Trendelenburg positioning and appropriate fluid management the patient continued to decline and an epidural blood patch was requested for treatment. There are few reports of SSFS associated with delayed motor deficits designated as motor trephine syndrome. Cerebral hemodynamic is compromised in the presence of a cranial defect by the following mechanisms. He syndrome of the trephined or the sinking skin flap SSF syndrome is a rare complication after a large skull bone defect1 It consists of a sunken skin above the bone defect with neurological symptoms such as severe headaches mental changes focal deficits or seizures12 The SSF may. This results in displacement of the brain across various intracranial boundaries. A case presentation and review Dr Bipin Bhimani Well Care Hospital Rajkot 2. Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome Published. SUNKEN SKIN FLAP SYNDROME. We also evaluated the risk factors for the incidence of SSFS.
This results in displacement of the brain across various intracranial boundaries. Independent of the consequences of the original aetiology that necessitated the craniectomy the bone defect alone may be the cause of the symptoms called trephined syndrome or. SUNKEN SKIN FLAP SYNDROME. The sinking skin flap syndrome SSFS is defined as a secondary neurological deterioration which cannot be attributed to the primary illness and which occurs in the presence of a sinking skin flap in patients with large craniectomies. He syndrome of the trephined or the sinking skin flap SSF syndrome is a rare complication after a large skull bone defect1 It consists of a sunken skin above the bone defect with neurological symptoms such as severe headaches mental changes focal deficits or seizures12 The SSF may. This results in displacement of the brain across various intracranial boundaries. Paradoxical brain herniation also known as sinking skin flap syndrome or syndrome of the trephined is a rare and potentially fatal complication of decompressive craniectomy.





































Post a Comment for "Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome"