X Linked Autoimmune Disease
X linked autoimmune disease. The CYBB gene is located on the X chromosome which is one of the two sex chromosomes. As a consequence they have low numbers of T cells and natural killer cells and their B cells do not function. Boys with this type of SCID have white blood cells that grow and develop abnormally.
If a son inherits a disease-causing mutation in a gene located on the X. As with many autoimmune diseases females are more susceptible than males. X-linked SCID which is caused by mutations in a gene on the X chromosome primarily affects male infants.
There are at least four types of autosomal recessive hyper IgM syndrome. FOXP3is important in the development of regulatory T cells and complete loss of FOXP3expression has been shown to result in severe autoimmunity. National Library of Medicine X-linked recessive diseases are caused by genes located on the X chromosome.
59 linhas X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy X-ALD is a genetic disease that affects the. 27 28 The disease is characterized by an inability to mount an effective immune response to EBV. In males who have only one X chromosome one mutated copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition.
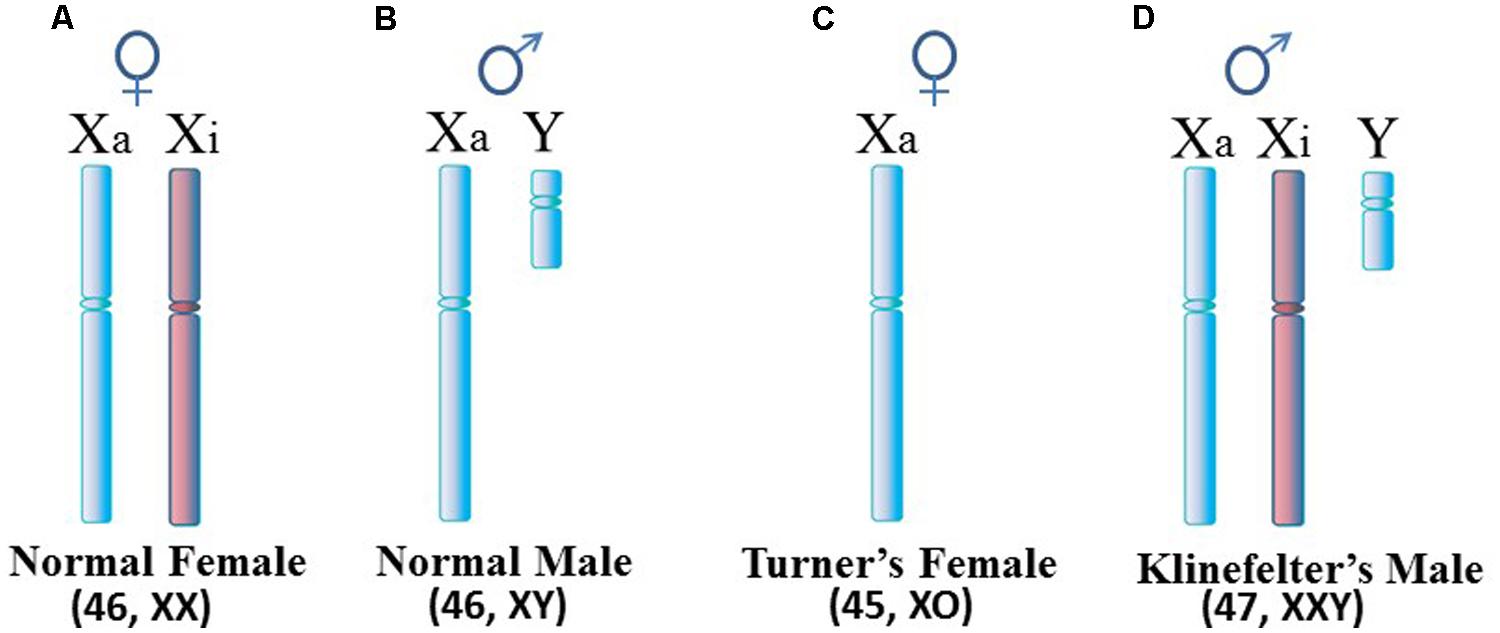
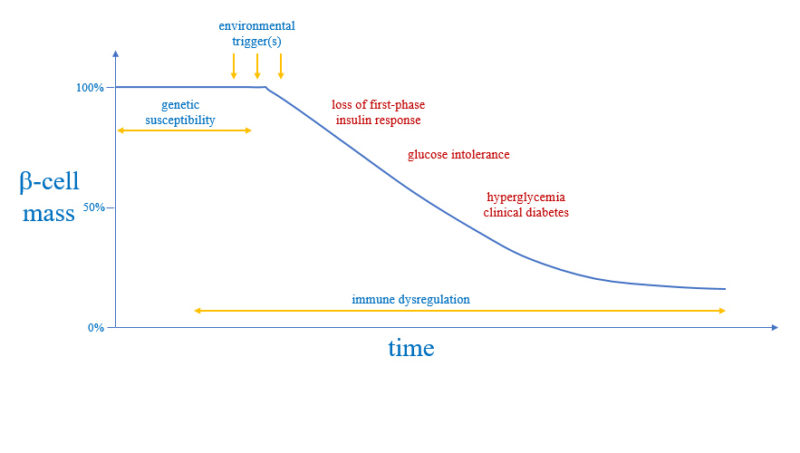
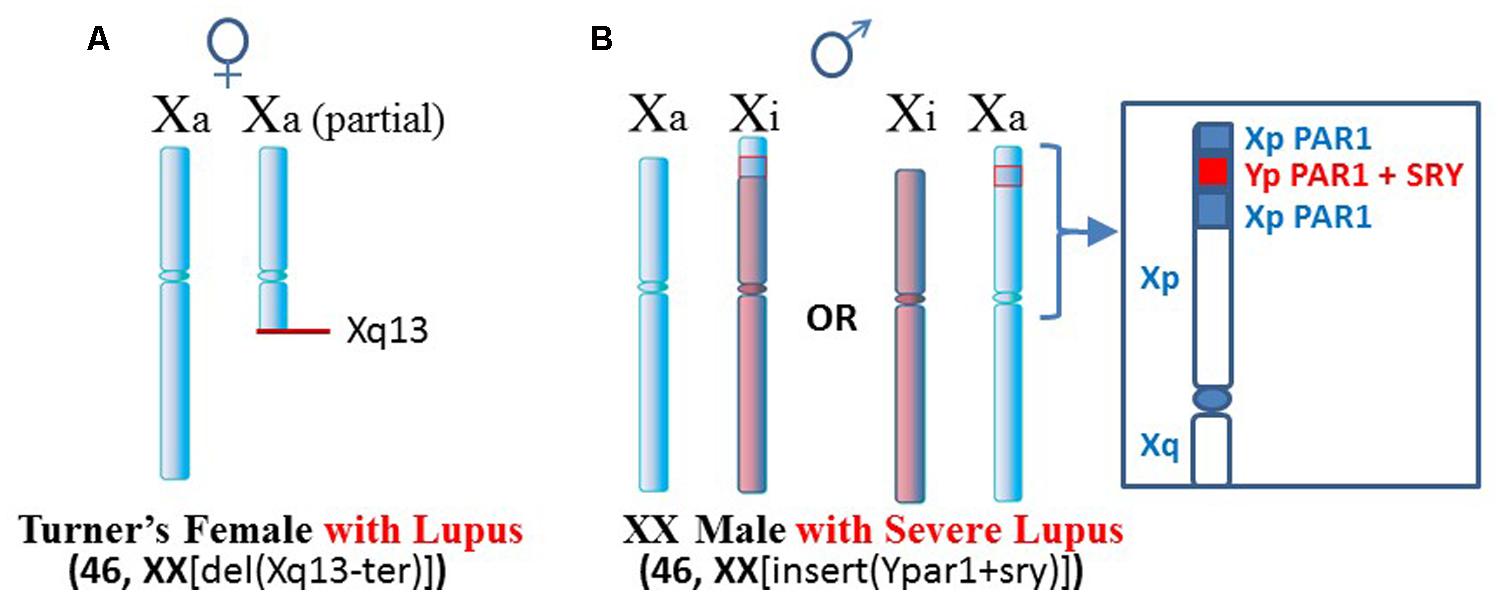
This review is focused on the role of impaired intestinal barrier function on autoimmune pathogenesis. When chronic granulomatous disease is caused by mutations in the CYBB gene the condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. We hypothesized that the autoimmune susceptibility in Turner Syndrome may be due to an alteration in the expression of the X-linked FOXP3gene.
X-linked lymphoproliferative disease XLP previously called Duncan disease 26 is due to a defect in SLAM-associated protein. The actual prevalence is not known. A web-based patient survey was conducted December 2011- February 2012.
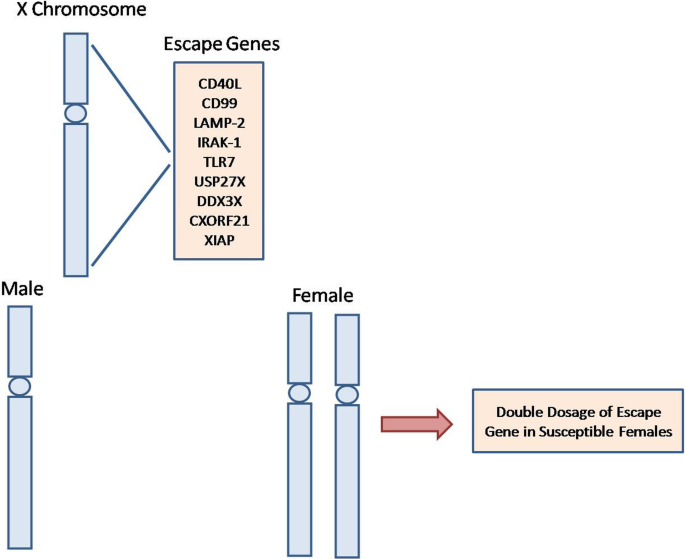
This is called X-linked hyper IgM syndrome or XHIM and is the most common type. This X-linked gene could have a more generalized role in autoimmunity pathogenesis.
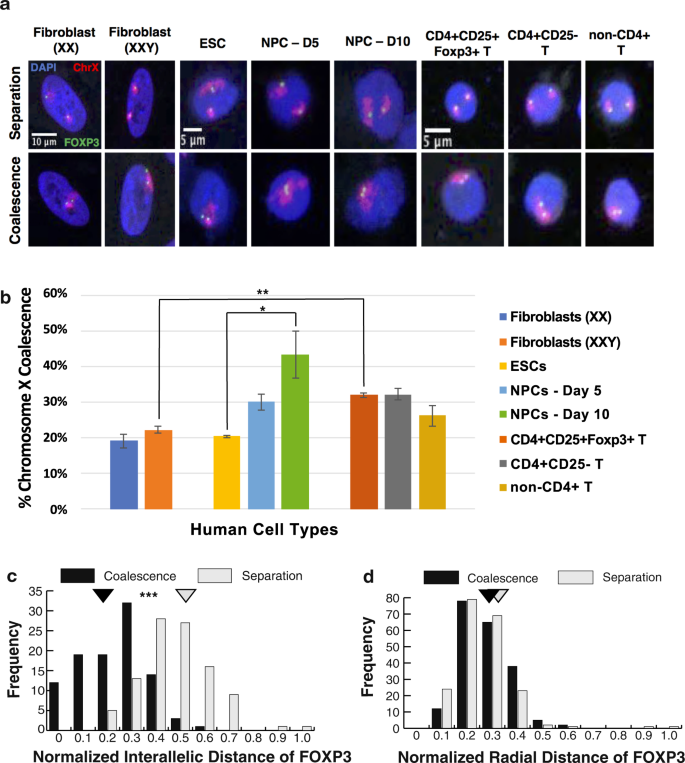
FOXP3is important in the development of regulatory T cells and complete loss of FOXP3expression has been shown to result in severe autoimmunity.
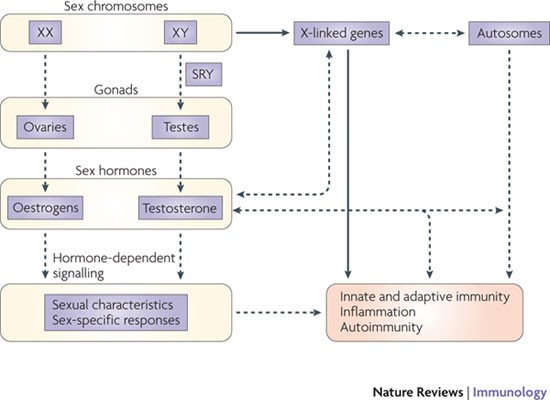
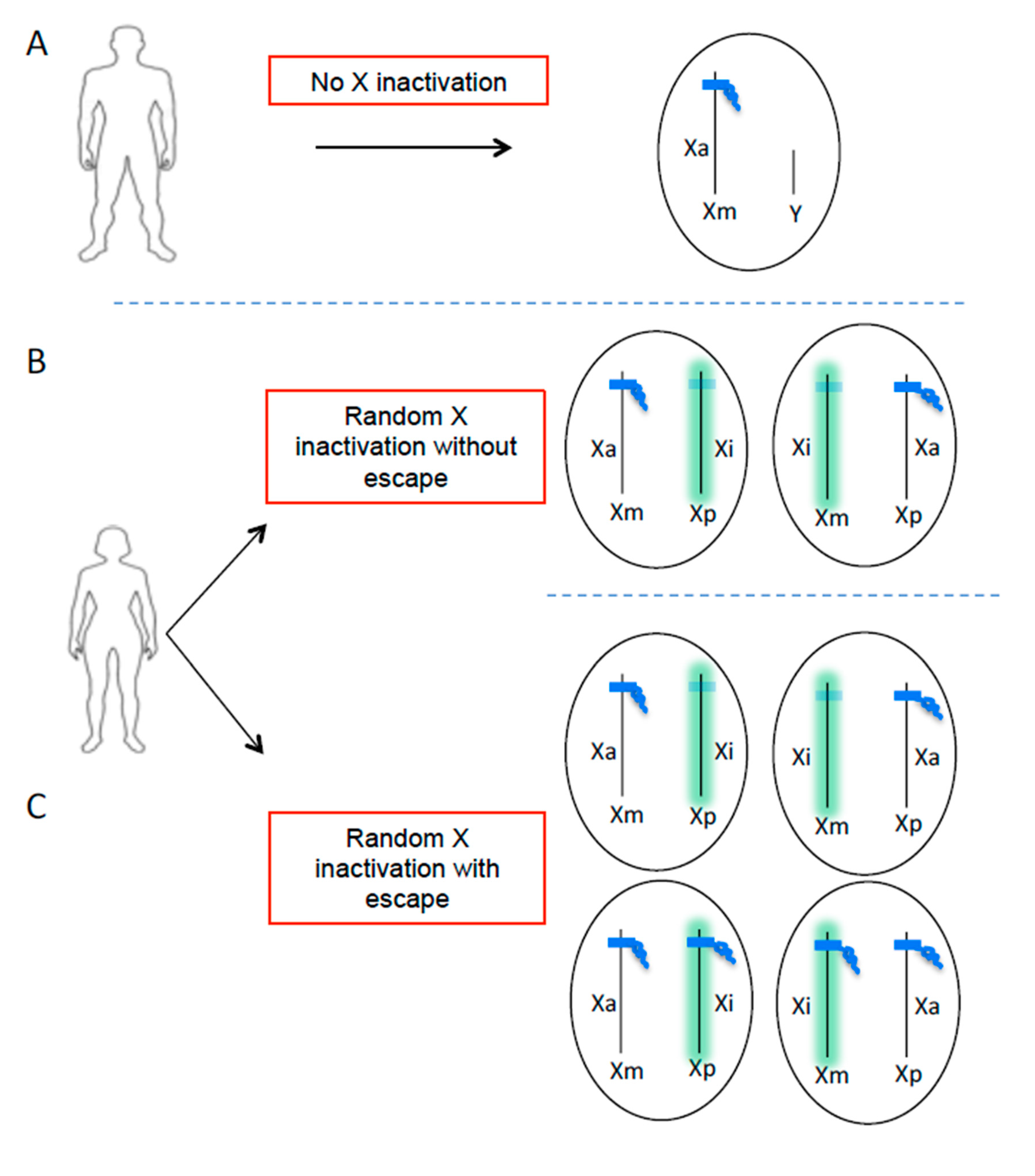
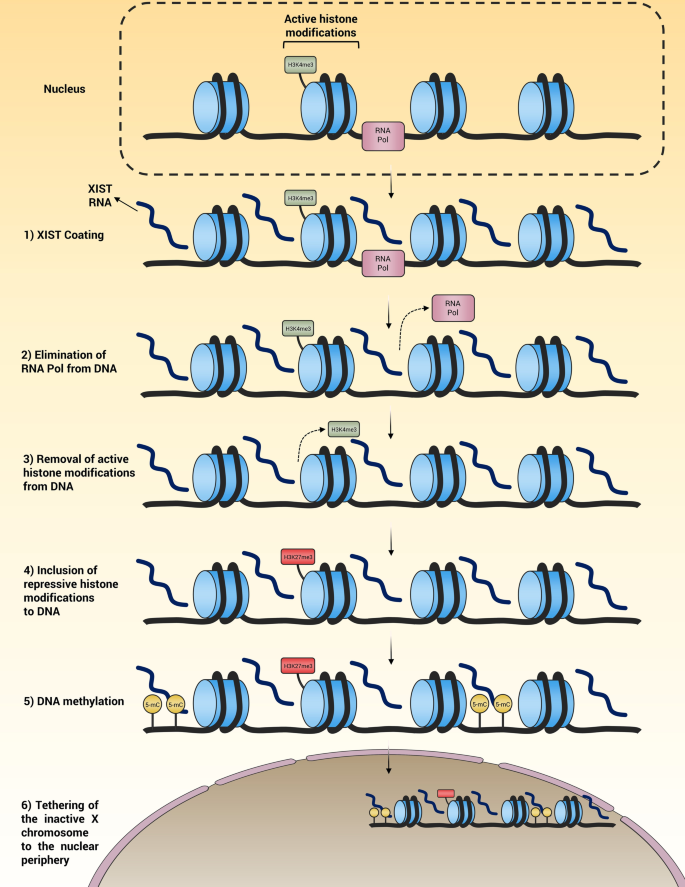
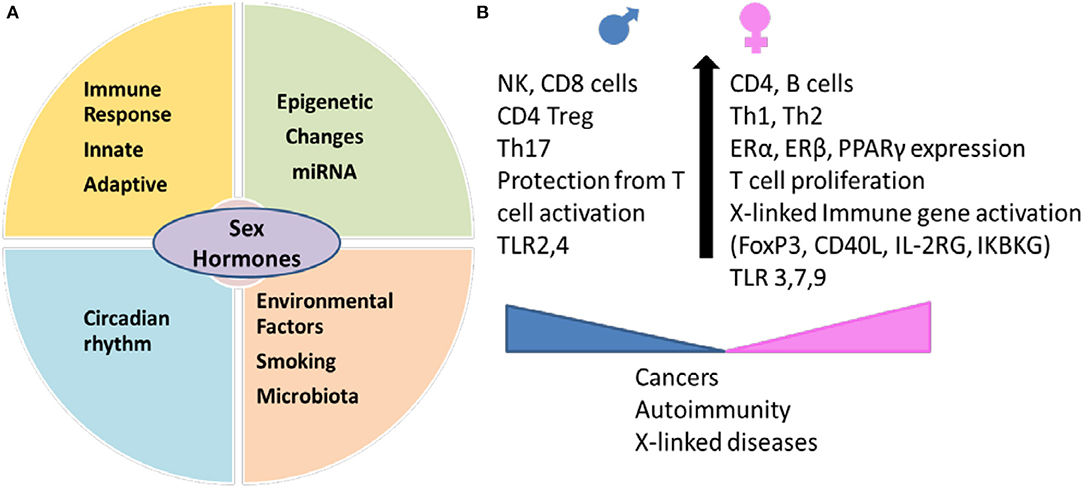
27 28 The disease is characterized by an inability to mount an effective immune response to EBV. These forms affect men and women equally. As with many autoimmune diseases females are more susceptible than males. It is intriguing that most X-linked primary immune deficiencies carry significant autoimmune manifestations thus illustrating the critical role played by products of single gene located on the X chromosome in the onset function and homeostasis of the immune system. This review is focused on the role of impaired intestinal barrier function on autoimmune pathogenesis. FOXP3is important in the development of regulatory T cells and complete loss of FOXP3expression has been shown to result in severe autoimmunity. There are at least four types of autosomal recessive hyper IgM syndrome. Together with the gut-associated lymphoid tissue and. People with XLP have an increased risk of infection because their body cannot properly regulate the number of immune system cells lymphocytes and blood cells.
When chronic granulomatous disease is caused by mutations in the CYBB gene the condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. X-linked SCID which is caused by mutations in a gene on the X chromosome primarily affects male infants. X-linked lymphoproliferative disease XLP previously called Duncan disease 26 is due to a defect in SLAM-associated protein. Multiple sclerosis MS is a putative T cell-mediated autoimmune disease. Sexual dimorphisms may be due to differences in sex hormones sex chromosomes or both. In the past XLA was described as associated with several inflammatory conditions but with adequate immune globulin treatment these are presumed to have diminished. In males who have only one X chromosome one mutated copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition.
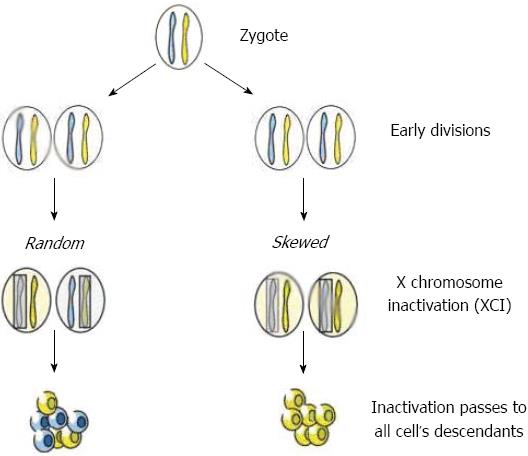


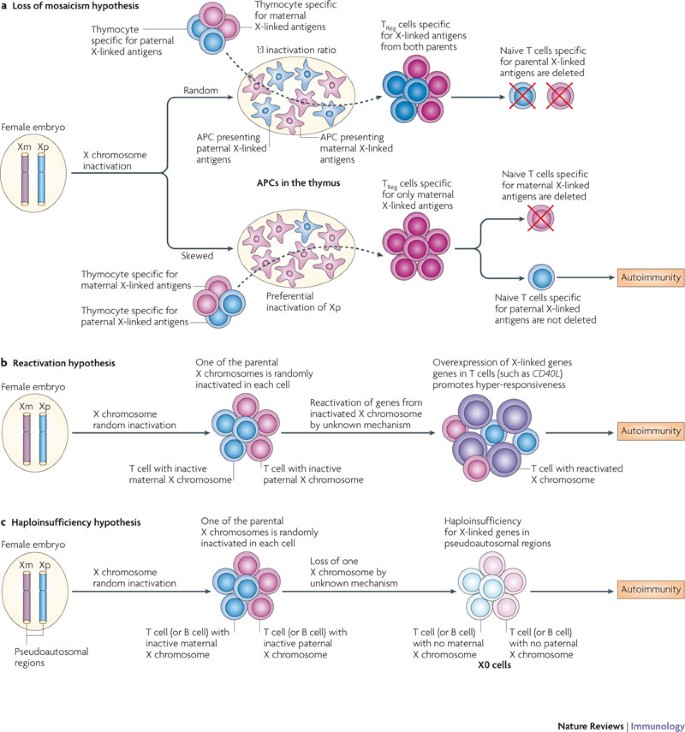
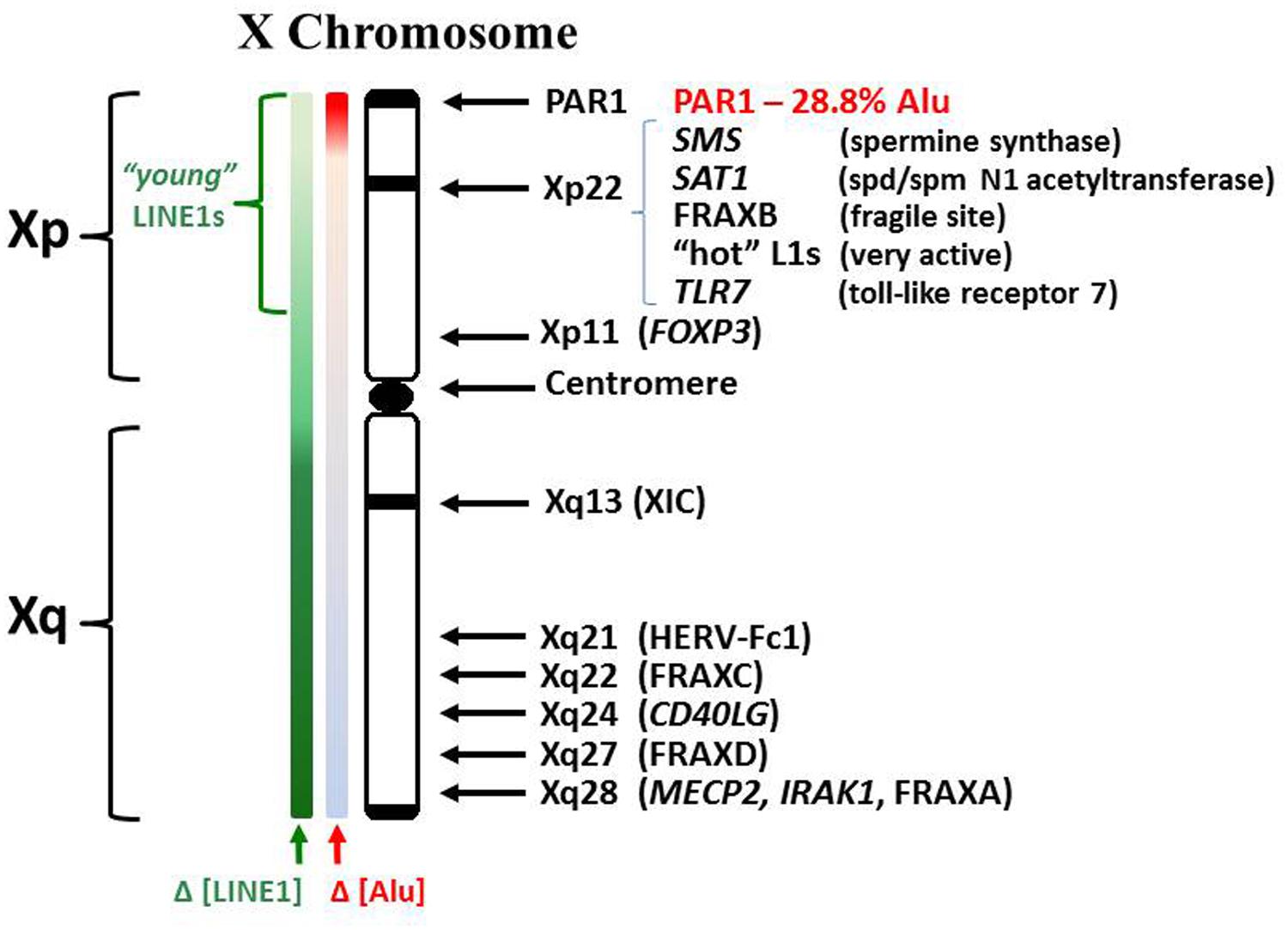

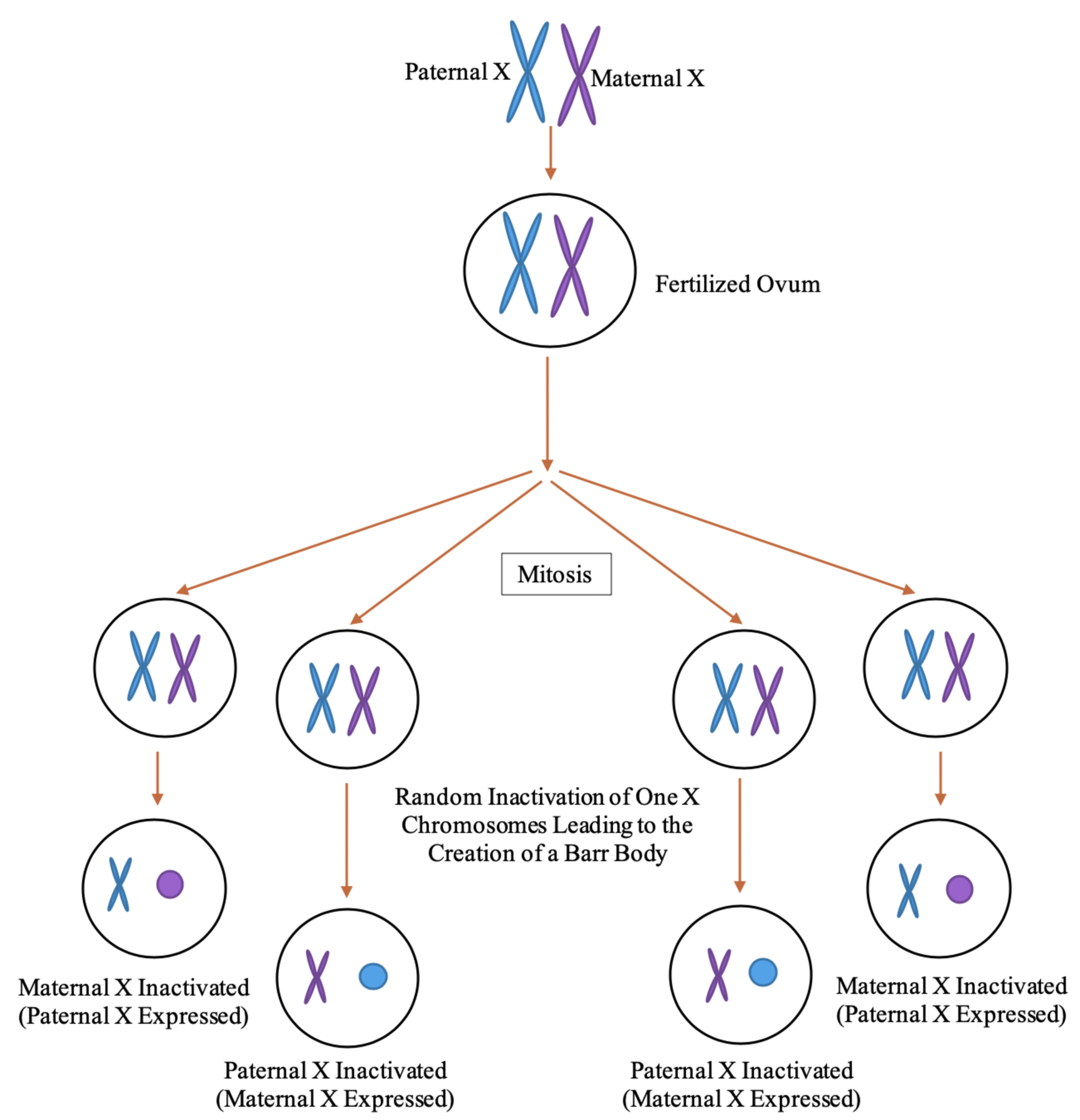











/why-autoimmune-diseases-affect-more-women-5095040_final-6b673e3c01cf466688de16ffe7029c07.jpg)



/3232654_color1_edited-5c362536c9e77c0001885f8b.png)









Post a Comment for "X Linked Autoimmune Disease"